August 22, 2025
Primary Amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM)
Why in the News?
Health Department officials are probing the well water as the possible cause of the primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM) infections after Naegleria fowleri was detected in a well in a case that involved a three-month-old child. This is after recent PAM cases, including a death resurfaced causing increased levels of investigation into water sources such as wells and ponds.
What is Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM) ?
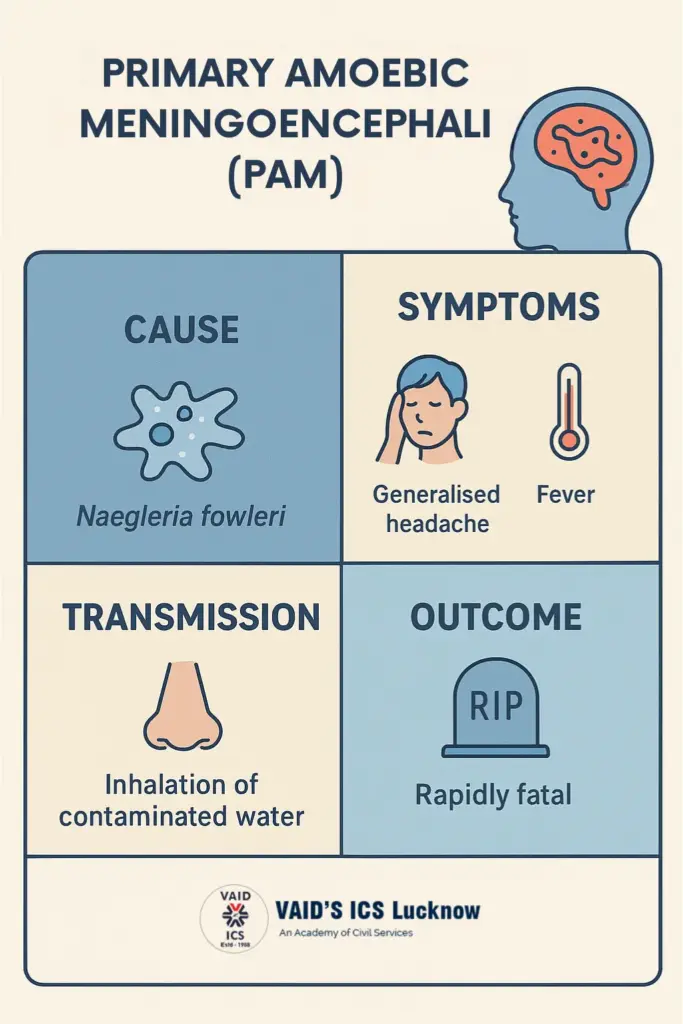
It is a rare but deadly brain infection caused by the free-living amoeba Naegleria fowleri, often called the “brain-eating amoeba.”
- Cause: Naegleria fowleri, an organism found in warm fresh water such as in ponds, lakes, rivers, hot springs, and, in rare occasions even in wells and pools that are not well maintained.
- Transmission: Amoeba enters the body through the nose, most often during swimming, diving, etc. in contaminated water. It is then diffused to the brain through the olfactory nerve and inflames to a severe point.
- Symptoms: The first signs (in 1-9 days) are fever, headache, nausea and vomiting. As the infection advances, it leads to confusion, seizures, stiff neck, loss of balance, hallucinations and coma. Death normally follows 1-18 days after the start of symptoms.
- Fatality Rate: The rate of fatality in PAM is almost complete with a mortality rate greater than 97%. There is a report of few survivors spread around the world
- Diagnosis: Acts as a problematic condition because of its rarity, and speed of progression. It must have special tests such as analysis of cerebrospinal fluid or PCR to identify the amoeba.
- Treatment: There is no standard effective treatment. Combinations of such drugs as amphotericin B and miltefosine are adopted, however, the result remains poor. It is imperative but difficult to diagnose in the early stage
Risk Factors: Exposure to stagnant freshwater at tempers ranging between 25 and 40 o C and worse in the summertime. Risk can be elevated by practices such as use of nasal rinsing or dripping of water inside the nose during a bath.
October 6, 2025
September 24, 2025
September 23, 2025
September 22, 2025