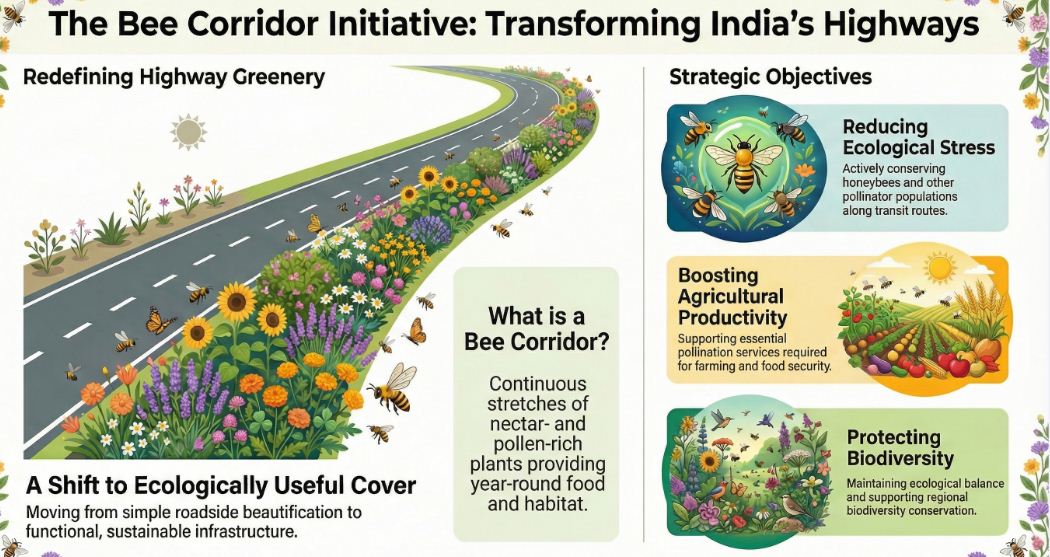
राष्ट्रीय राजमार्ग प्राधिकरण (NHAI) ने सतत अवसंरचना (Sustainable Infrastructure) कार्यक्रम के अंतर्गत एक अद्वितीय पहल की घोषणा की है, जिसके तहत राष्ट्रीय राजमार्गों के किनारे परागणकर्ता गलियारे (Pollinator Corridor) अथवा ‘बी कॉरिडोर’ विकसित किए जाएंगे। यह पहल सड़क किनारे केवल सजावटी पौधारोपण की जगह पर्यावरणीय रूप से उपयोगी हरित आवरण विकसित करने की दिशा में महत्वपूर्ण कदम है।
बी कॉरिडोर क्या है?
बी कॉरिडोर से तात्पर्य राष्ट्रीय राजमार्गों के किनारे विकसित ऐसे हरित क्षेत्र से है, जहाँ मधुमक्खियों एवं अन्य परागणकर्ताओं के लिए अनुकूल पौधों, झाड़ियों और वृक्षों का निरंतर रोपण किया जाएगा। इसका उद्देश्य पूरे वर्ष पराग (Pollen) और मधुरस (Nectar) की उपलब्धता सुनिश्चित करना है।
पहल के उद्देश्य:
इस योजना के प्रमुख उद्देश्य निम्नलिखित हैं:
-
मधुमक्खियों तथा अन्य परागणकर्ताओं का संरक्षण करना।
-
परागणकर्ताओं पर बढ़ते पारिस्थितिक दबाव (Ecological Stress) को कम करना।
-
परागण सेवाओं को सुरक्षित करना, जो निम्न क्षेत्रों में अत्यंत महत्वपूर्ण हैं:
-
कृषि उत्पादकता
-
खाद्य सुरक्षा
-
जैव विविधता संरक्षण
-
पारिस्थितिक संतुलन बनाए रखना
-
-
राष्ट्रीय राजमार्ग विकास को पर्यावरण-अनुकूल एवं सतत बनाना।
योजना की प्रमुख विशेषताएँ:
1. सजावटी नहीं, पारिस्थितिक पौधारोपण
-
यह योजना सड़क किनारे केवल सुंदरता बढ़ाने वाले पौधों के बजाय पर्यावरणीय उपयोगिता वाले वृक्षों और वनस्पतियों पर केंद्रित होगी।
-
गलियारे में वृक्ष, झाड़ियाँ, औषधियाँ (Herbs) तथा घास का संतुलित मिश्रण होगा।
2. वर्षभर पुष्पन (Year-round flowering)
-
पौधों का चयन इस प्रकार किया जाएगा कि विभिन्न ऋतुओं में अलग-अलग प्रजातियाँ खिलें, जिससे पूरे वर्ष मधुमक्खियों को भोजन उपलब्ध हो सके।
-
इससे लगभग निरंतर पुष्पन चक्र (Continuous blooming cycle) बना रहेगा।
3. परागणकर्ताओं के लिए प्राकृतिक आवास
-
योजना के अंतर्गत केवल पौधारोपण ही नहीं, बल्कि मधुमक्खियों के अनुकूल प्राकृतिक वातावरण तैयार किया जाएगा।
-
इसके लिए:
-
फूल देने वाली जंगली घासों को बढ़ने दिया जाएगा।
-
सूखी लकड़ी, खोखले तने एवं पुराने वृक्षों के हिस्सों को संरक्षित रखा जाएगा, जो परागणकर्ताओं के लिए आश्रय स्थल बनते हैं।
-
प्रस्तावित पौधों/वृक्षों की प्रजातियाँ
एनएचएआई द्वारा चयनित प्रमुख पराग एवं मधुरस युक्त वृक्षों में शामिल हैं:
-
नीम
-
करंज
-
महुआ
-
पलाश
-
बॉटल ब्रश
-
जामुन
-
सिरिस
ये प्रजातियाँ मधुमक्खियों को आकर्षित करने और परागण सेवाओं को बढ़ाने में सहायक मानी जाती हैं।
कार्यान्वयन रणनीति
-
यह गलियारा कृषि-जलवायु अनुकूलता (Agro-climatic suitability) के आधार पर राष्ट्रीय राजमार्गों के किनारे तथा एनएचएआई की रिक्त भूमि पर विकसित किया जाएगा।
-
एनएचएआई के फील्ड कार्यालय उन स्थानों की पहचान करेंगे जहाँ:
-
हर 500 मीटर से 1 किलोमीटर के अंतराल पर फूलदार वृक्षों के समूह लगाए जा सकें।
-
-
यह दूरी मधुमक्खियों की औसत खोज दूरी (Foraging range) के अनुरूप रखी गई है।
लक्ष्य (2026-27)
-
एनएचएआई का लक्ष्य वर्ष 2026-27 में कम से कम तीन परागणकर्ता गलियारे विकसित करना है।
-
इसी अवधि में राष्ट्रीय राजमार्गों के किनारे लगभग 40 लाख वृक्ष लगाए जाएंगे।
-
इनमें से लगभग 60% वृक्षारोपण बी कॉरिडोर पहल के अंतर्गत किया जाएगा।
महत्त्व
यह पहल अत्यंत महत्वपूर्ण है क्योंकि:
-
परागणकर्ता कृषि उत्पादन में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाते हैं।
-
मधुमक्खियों की संख्या में गिरावट से फसल उत्पादन, फल-फूलों की पैदावार तथा जैव विविधता पर गंभीर प्रभाव पड़ता है।
-
यह योजना राजमार्ग विकास को हरित, टिकाऊ एवं पर्यावरण-संतुलित बनाने में सहायक होगी।
-
इससे भारत में सतत विकास के लक्ष्यों को भी बल मिलेगा।
निष्कर्ष
एनएचएआई की ‘बी कॉरिडोर’ पहल एक अभिनव प्रयास है, जो सड़क निर्माण एवं पर्यावरण संरक्षण के बीच संतुलन स्थापित करने की दिशा में महत्वपूर्ण कदम है। यह योजना परागणकर्ताओं के संरक्षण के साथ-साथ कृषि उत्पादकता और पारिस्थितिक स्थिरता को भी मजबूत करेगी