August 22, 2025
National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organisation (NOTTO)
Why in the News?
- The National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organisation (NOTTO) has issued a new 10-point advisory to address gender disparity in organ transplants.
- The advisory directs that women patients and relatives of deceased donors will get priority in organ allocation.
Key Points: National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organisation (NOTTO)
Gender Disparity in Organ Transplants:
- Between 2019 and 2023, women accounted for nearly 64% of all living organ donors.
- Yet, men received 69.8% of transplanted organs.
- Out of 56,509 organ donations, women donated 36,038, but only 17,041 were transplanted into women.
Legal Framework:
- Organ donation governed by the Transplantation of Human Organs Act, 1994 (amended in 2011 to include tissues).
- Prohibits organ trade with strict financial & judicial penalties.
NOTTO’s Advisory Highlights:
- The allocation of funds will be prioritized for women and the families of deceased donors.
- States have been encouraged to create permanent positions for transplant coordinators in hospitals.
- Trauma centres to be developed as organ retrieval centres.
- Training for ambulance staff & emergency responders to identify potential deceased donors early (esp. accident & stroke victims).
Status of Organ Donation in India:
- According to the WHO, just one-tenth of the world’s need for organs is currently fulfilled.
- Every year in India, nearly 1.8 lakh people reach end-stage kidney disease, yet only about 12,000 undergo kidney transplants
- It is estimated that one organ donor can save eight lives
- Challenges:
- Lack of awareness, cultural myths, and family hesitation remain major barriers.
- Appeals increase awareness but allocation still follows waiting list rules.
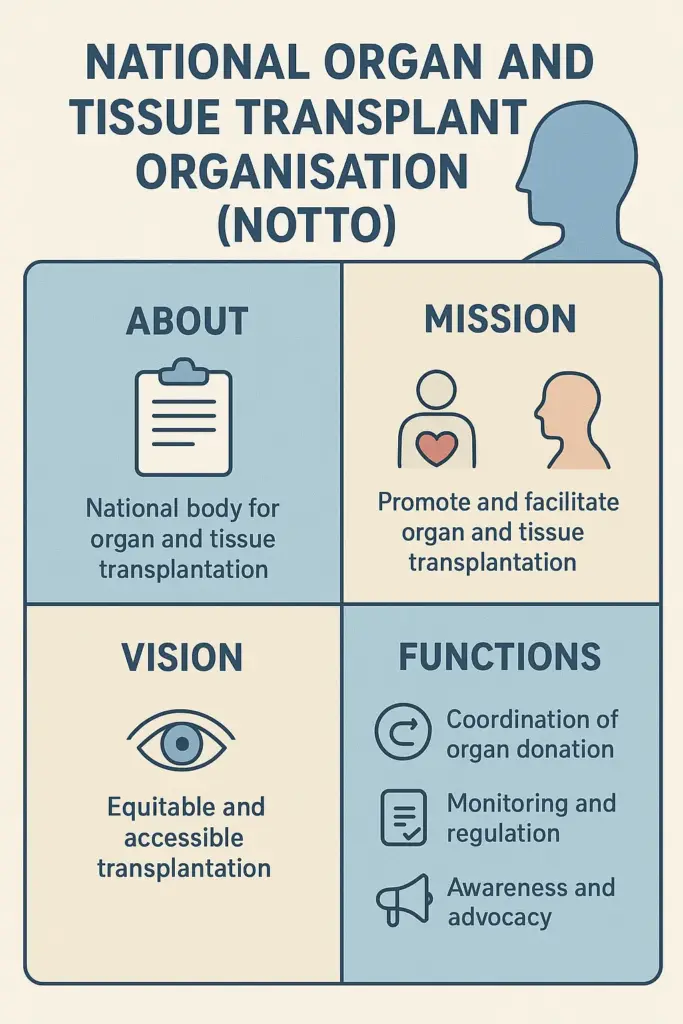
About National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organisation (NOTTO):
The Apex level national organisation in terms of organ and tissue donation and transplantation in India is TTO.
- It operates under the Directorate General of Health Services (DGHS) under the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare Government of India.
- Aimed at streamlining organ collection, allocation, and transplantation across the country.
Objectives of NOTTO:
- To maintain a national registry of organ and tissue donors and recipients.
- To ensure fair and transparent allocation of organs.
- The purpose of this is to share knowledge and improve understanding of organ donation.
- To coordinate with regional and state-level organizations for organ distribution.
- To educate health care professionals, coordinators and emergency personnel in organ procurement and transplantation.
About Transplantation of Human Organs Act, 1994 (THOA)
By the Transplantation Human Organs Act (THOA), 1994, the Parliament had regulated the removal, storing and transplantation of human organs to be used in therapies.
- It was enacted to curb organ trade, elevate the ethical nature of organ donation and legally insure transplant action in India.
- Later the Act was amended to incorporate tissues as well as organs in 2011.
GIST OF DAILY ARTICLES THE HINDU/INDIAN EXPRESS : 4 sep 2025
September 4, 2025
Gist of Daily News Papers Articles/The Hindu /Indian Express-1 Sep 2025
September 1, 2025
GIST OF DAILY ARTICLES THE HINDU/INDIAN EXPRESS/27 August 2025
August 27, 2025