February 3, 2026
India-Arab relations/ Delhi Declaration 2026
Why in News ? The Delhi Declaration (January 31, 2026) marks a significant milestone in India-Arab relations, transitioning from historical ties to a modern, strategic partnership.
- Institutional Framework & Future Roadmap:
- Executive Program (2026-2028): A concrete timeline was set for various summits, including the 3rd Ministerial Meeting (2028), a Startup Conclave (2027), and working groups on Space and Tourism.
- High-Level Consultations: Agreement to hold regular sectoral consultations led by respective Ministers to ensure specific activities are implemented rather than just discussed.
- Economic and Technological Synergy:
- Trade & Investment: Welcomed robust trade exceeding US$240 billion. Focused on emerging sectors like green hydrogen, infrastructure, and startups.
- Energy Security: Transitioning from traditional oil/gas cooperation to Renewable Energy and green technologies. India encouraged Arab participation in the Global Biofuel Alliance and ISA.
- Digital & AI: Emphasized cooperation in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and digital technologies while respecting national sovereignty and ethical frameworks.
- Connectivity and Food Security:
- Food Security: Enhanced cooperation in agriculture and fertilizers to stabilize food supply chains. A dedicated Agriculture & Food Security Conference is slated for 2027.
- Maritime Initiatives: The Arab side briefed India on the STREAM initiative (Suez Canal-Red Sea development) to boost maritime logistics and “Blue Economy” in the Red Sea region.
- Healthcare and Space Cooperation:
- Pharmaceuticals: India sought recognition of the Indian Pharmacopoeia in Arab nations to provide affordable, high-quality drugs.
- Space: Establishment of the India-Arab Space Cooperation Working Group (2027) to harness satellite technology for developmental goals.
- Geopolitical and Security Positions:
- Palestine: Reaffirmed support for a two-state solution based on 1967 borders. Welcomed the 2025 Gaza ceasefire and noted the formation of a Palestinian technocratic committee for Gaza’s administration.
- Regional Stability: Reaffirmed support for the sovereignty and territorial integrity of Lebanon, Libya, Sudan, Somalia, and Yemen.
- Counter-Terrorism:
- Strongly condemned the Pahalgam terrorist attack (targeting Indian tourists).
- Adopted a “zero tolerance” approach and condemned the use of drones by terrorists for trafficking and attacks.
- Welcomed the Algeria Guiding Principles on preventing terror financing via emerging tech.
- Global Governance & The Global South:
- UNSC Reform: Called for an expansion of the UN Security Council in both permanent and non-permanent categories to reflect contemporary realities.
- Voice of Global South: The Arab League praised India’s leadership in representing the Global South and agreed to coordinate closely at the UN in New York and Geneva.
- Soft Power and Diaspora:
- Indian Diaspora: Acknowledged the 9 million-strong Indian community in Arab states as a “living bridge.”
- Culture & Education: Welcomed the registration of “Henna” on the UNESCO heritage list and the 1st India-Arab University Presidents Conference.
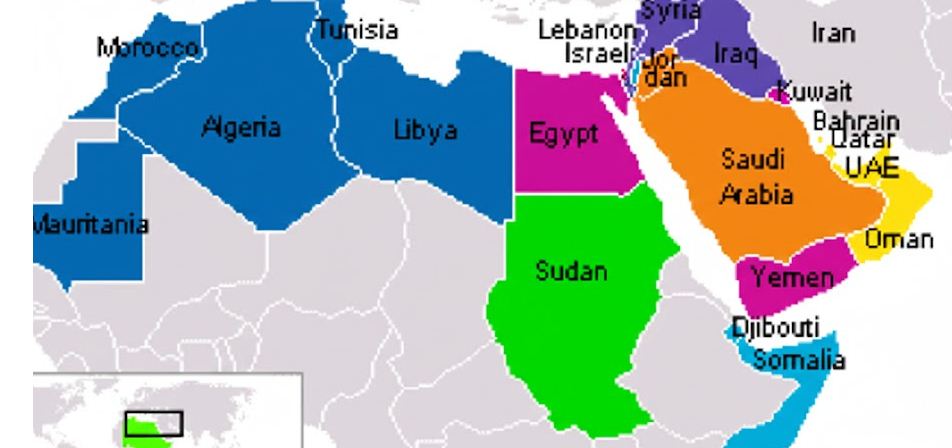
About Arab League:
- Arab League members (22 countries)
- Arab League consists of 22 member states spanning West Asia and North Africa, formed to promote political, economic, and cultural coordination among Arab countries.
West Asia (Middle East):
- Saudi Arabia, United Arab
- Emirates, Qatar, Kuwait, Oman, Bahrain, Iraq, Jordan, Lebanon, Syria, Yemen, Palestine
North Africa:
Egypt, Libya, Tunisia, Algeria, Morocco, Mauritania, Sudan, Somalia, Djibouti, Comoros
HQ:
- Egypt (Cairo) hosts the headquarters of the Arab League.
- Palestine is a full member.
- Comorosis the only island nation in the Arab League.
India & Arab League:
Institutional Evolution & Background:
- Foundation: The Arab League, established in 1945, consists of 22 member states across West Asia and North Africa.
- Formalization: India formalised its engagement in 2002 via an MoU that initiated structured political dialogue.
- Expansion: The Arab–India Cooperation Forum (2008) was a turning point, followed by the appointment of India’s Ambassador to Egypt as the Permanent Representative to the Arab League in 2010.
Political and Strategic Convergence:
- Strategic Partnerships: Since 2008, India has upgraded ties with major Arab powers, focusing on regional stability and counter-terrorism.
- Vision Alignment: There is a significant synergy between India’s Viksit Bharat 2047 and Arab national blueprints like Saudi Vision 2030, aligning long-term development goals.
Trade, Investment, and Connectivity:
- Economic Scale: Bilateral trade exceeds USD 240 billion. The UAE remains India’s top partner within the league, with trade surpassing USD 115 billion.
- Inbound Investment: Massive sovereign wealth fund commitments have been pledged:
- UAE: USD 75 billion
- Saudi Arabia: USD 100 billion
- Qatar: USD 10 billion
- Strategic Corridors: The India–Middle East–Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) serves as a modern silk route, enhancing connectivity through the Red Sea and Suez Canal.
Energy and Food Security:
- Primary Supplier: The Arab region is the backbone of India’s resource security, providing:
-
- 60% of crude oil imports.
- 70% of natural gas (LNG).
- 50%+ of fertiliser imports (critical for India’s agriculture).
- LNG Landmark: A massive USD 78 billion deal with Qatar ensures 7.5 million tonnes of gas annually for the next 20 years.
Digital and Financial Cooperation:
- FinTech Expansion: India’s Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) is going global through:
- Deployment of RuPay cards and UPI in multiple Arab nations.
- A Rupee–Dirham settlement mechanism to bypass third-party currencies.
- Currency Confidence: Since 2023, the acceptance of the Indian Rupee at Dubai airports symbolizes the growing global trust in the Indian economy.
Defence and Security Cooperation:
- Maritime Reach: Partnerships with Oman, UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Egypt include joint naval exercises and maritime security.
- Strategic Access: India’s access to Oman’s Duqm Port is a vital strategic asset, extending the Indian Navy’s reach in the western Indian Ocean.
- Counter-Terrorism: Arab nations have consistently supported India’s position on cross-border terrorism, reflecting a shared zero-tolerance policy.
October 17, 2025
October 16, 2025
October 6, 2025
September 24, 2025
