September 24, 2025
H-1B Visa: 7 Devastating Impacts on Indian IT Industry
H-1B Visa : Impact on Indian IT Industry
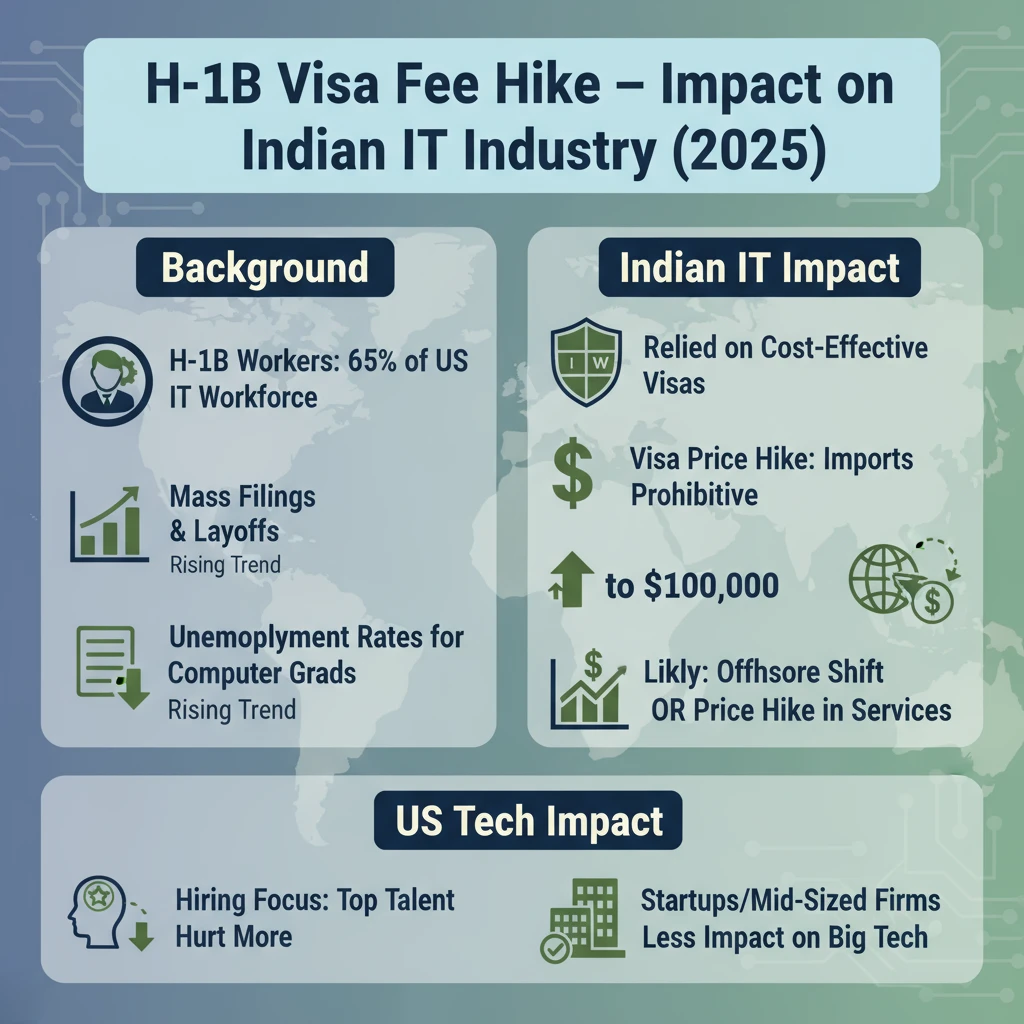
The Trump administration has introduced a $100,000 annual fee on H-1B visas: The policy aims to curb labour arbitrage by India’s IT giants and Big Tech firms while protecting U.S. universities and startups. The broader impact on the U.S. innovation ecosystem remains uncertain.
Background:
- H-1B workers now account for 65% of America’s IT workforce, up from 32% in 2003.
- Despite this, computer science graduates face unemployment of 6.1%, and computer engineering graduates face 7.5%.
- Some tech companies filed over 10,000 H-1B applications in FY2024 while conducting mass layoffs of U.S. workers.
Impact on Indian IT Industry:
- Companies like Tata Consultancy Services, Infosys, and Wipro relied on H-1B visas costing a few thousand dollars to import engineers at lower wages.
- At $100,000 per visa, this becomes economically prohibitive: Companies must either raise prices or shift work offshore, reducing their competitive edge.
Impact on U.S. Tech Companies:
- Each H-1B hire now represents significant capital allocation, requiring executive approval.
- This may filter applications toward exceptionally skilled candidates, aligning with the program’s original purpose.
- Startups and mid-sized companies may be disproportionately affected compared to large firms like Google and Microsoft.
Collateral Consequences:
- International students contribute over $40 billion annually to the U.S. economy; more than half are in STEM fields.
- The fee may discourage global talent, pushing them toward Canada, Australia, or the UK.
- This risks losing the next generation of technological innovators to competing nations, especially amid geopolitical tensions with China.
Policy Criticism:
- Design simplicity over sophistication: Fee applies uniformly rather than being based on salary levels, elite graduates, or research fields.
- Could be seen as a sledgehammer approach, harming innovation and talent attraction.
- May accelerate offshoring of jobs instead of creating more opportunities for U.S. workers.
Key Takeaways:
- Objective: Reduce H-1B wage arbitrage and protect domestic workers.
- Risks: Diminished U.S. global talent attraction, concentration of opportunities in large firms, potential offshoring of jobs.
- Indian IT Impact: Higher costs may force price hikes or offshore delivery models, challenging competitiveness.
- Global Implications: Competitor countries may capture exceptional talent that the U.S. may no longer attract.
Conclusion:
The $100,000 H-1B fee is a radical measure targeting labour arbitrage but carries significant collateral risks: It may reduce U.S. competitiveness, accelerate offshoring, and divert global talent to other nations. The balance between domestic worker protection and innovation retention will determine the policy’s long-term success.
September 24, 2025
September 23, 2025
September 22, 2025
September 17, 2025