January 29, 2026
Economic Survey 2025-26: Key Highlights :
Economic Survey 2025-26: Key Highlights :

Key Highlights :
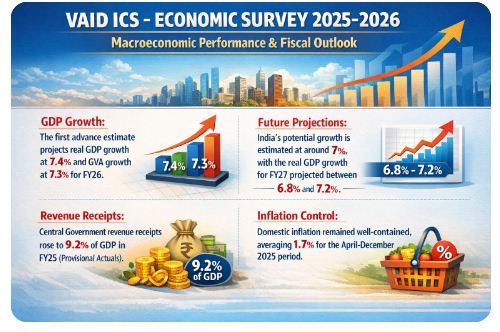
Macroeconomic Performance & Fiscal Outlook
- GDP Growth: The first advance estimate projects real GDP growth at 7.4% and GVA growth at 7.3% for FY26.
- Future Projections: India’s potential growth is estimated at around 7%, with the real GDP growth for FY27 projected between 6.8% and 7.2%.
- Revenue Receipts: Central Government revenue receipts rose to 9.2% of GDP in FY25 (Provisional Actuals).
- Inflation Control: Domestic inflation remained well-contained, averaging 1.7% for the April-December 2025 period.
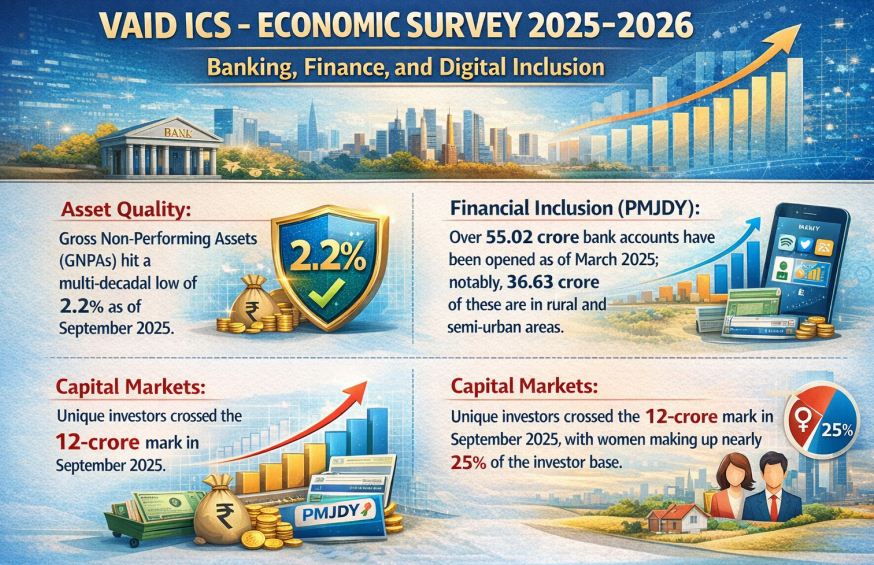
Banking, Finance, and Digital Inclusion:
- Asset Quality: Gross Non-Performing Assets (GNPAs) hit a multi-decadal low of 2.2% as of September 2025.
- Financial Inclusion (PMJDY): Over 55.02 crore bank accounts have been opened as of March 2025; notably, 36.63 crore of these are in rural and semi-urban areas.
- Capital Markets: Unique investors crossed the 12-crore mark in September 2025, with women making up nearly 25% of the investor base.
External Sector & Global Integration:
- Trade Expansion: India’s share of global merchandise exports nearly doubled from 1% to 1.8% between 2005 and 2024.
- Services Leadership: Services exports touched an all-time high of $387.6 billion in FY25, growing by 13.6%.
- Remittances: India remains the world’s largest recipient of remittances, with inflows reaching $135.4 billion in FY25.
- Forex Reserves: Reserves climbed to $701.4 billion (as of January 16, 2026), sufficient to cover 11 months of imports and 94% of external debt.
Agriculture & Rural Transformation:
- Record Production: Foodgrain production is estimated at 3577.3 LMT for AY 2024-25, an increase of over 254 LMT from the previous year.
- Direct Benefit Transfer: Over ₹4.09 lakh crore has been released to farmers under the PM-Kisan scheme since its inception.
- MGNREGS Reform: The Viksit Bharat-GramG initiative has been proposed as a statutory overhaul to align rural employment with the vision of a developed India by 2047.
Industry, Infrastructure, and Innovation:
- Manufacturing Recovery: GVA in manufacturing grew by 7.72% in Q1 and 9.13% in Q2 of FY26.
- PLI Impact: Production Linked Incentive schemes have attracted over ₹2.0 lakh crore in actual investment and generated 12.6 lakh jobs.
- Semiconductors: The India Semiconductor Mission has advanced with 10 projects involving an investment of ₹1.60 lakh crore.
- Logistics & Transport: * High-speed corridors increased from 550 km in FY14 to 5,364 km in FY26.
- 3,500 km of new railway lines were added in FY26 alone.
- Airports increased from 74 (2014) to 164 (2025), making India the world’s 3rd largest domestic aviation market.
Energy, Space, and Technology:
- Renewables: India now ranks 3rd globally in overall Renewable Energy and installed Solar capacity.
- Power Sector: Discoms recorded a historic turnaround with a positive Profit After Tax (PAT) of ₹2,701 crore in FY25.
- Space Frontier: India became the fourth nation to achieve autonomous satellite docking (SPADEX) capability.
Social Sector, Education, and Health:
- Education Infrastructure: India now hosts 23 IITs, 21 IIMs, and 20 AIIMS, including international IIT campuses in Zanzibar and Abu Dhabi.
- Enrollment: Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) stands at 90.9 at the primary and 78.7 at the secondary stage.
- Health Progress: India has outpaced global averages in reducing maternal and child mortality since 1990.
- Labor Welfare: The e-Shram portal has registered over 31 crore unorganized workers (54% women).
- Poverty Alleviation: The Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) plummeted from 55.3% (2005-06) to 11.28% (2022-23).
Strategic Vision: “Disciplined Swadeshi”
The Survey proposes a calibrated three-tiered strategy for strategic resilience:
- Building Critical Capabilities: Developing indigenous high-tech sectors.
- Reducing Input Costs: Enhancing manufacturing efficiency.
- Strategic Indispensability: Progressing from mere self-reliance to becoming a vital, irreplaceable link in global supply chains.

आर्थिक समीक्षा 2025-26 के मुख्य अंश:
व्यापक आर्थिक प्रदर्शन और राजकोषीय दृष्टिकोण:
भारतीय अर्थव्यवस्था ने वैश्विक अनिश्चितताओं के बावजूद अपनी मजबूती साबित की है।
- GDP वृद्धि: वित्त वर्ष 2026 (FY26) के लिए वास्तविक GDP वृद्धि 7.4% और GVA वृद्धि 7.3% रहने का अनुमान है।
- भविष्य का अनुमान: भारत की मध्यम अवधि की संभावित विकास दर 7% के आसपास है, जबकि वित्त वर्ष 2027 (FY27) के लिए GDP वृद्धि 6.8% से 7.2% के बीच रहने का अनुमान है।
- राजस्व प्राप्तियां: केंद्र सरकार की राजस्व प्राप्तियां वित्त वर्ष 2025 में बढ़कर GDP का 9.2% हो गईं।
- मुद्रास्फीति (महंगाई) पर नियंत्रण: घरेलू मुद्रास्फीति नियंत्रण में रही और अप्रैल-दिसंबर 2025 की अवधि में यह औसतन 1.7% रही।
बैंकिंग, वित्त और डिजिटल समावेशन:
बैंकिंग क्षेत्र की सेहत में सुधार और वित्तीय सेवाओं तक पहुंच में क्रांतिकारी बदलाव आए हैं।
- परिसंपत्ति गुणवत्ता (Asset Quality): बैंकों का सकल गैर-निष्पादित परिसंपत्तियां (GNPA) सितंबर 2025 तक कई दशकों के निचले स्तर 2.2% पर आ गया।
- वित्तीय समावेशन (PMJDY): मार्च 2025 तक 55.02 करोड़ से अधिक जन-धन खाते खोले गए, जिनमें से 36.63 करोड़ ग्रामीण क्षेत्रों में हैं।
- पूंजी बाजार: सितंबर 2025 में अद्वितीय निवेशकों (Unique Investors) की संख्या 12 करोड़ के पार निकल गई, जिसमें महिलाओं की हिस्सेदारी लगभग 25% है।
विदेशी क्षेत्र और वैश्विक एकीकरण:
- व्यापार विस्तार: वैश्विक माल निर्यात में भारत की हिस्सेदारी 2005 के 1% से लगभग दोगुनी होकर 2024 में 1.8% हो गई।
- सेवा निर्यात: वित्त वर्ष 2025 में सेवा निर्यात $387.6 बिलियन के सर्वकालिक उच्च स्तर पर पहुँच गया।
- विदेशी मुद्रा भंडार: 16 जनवरी 2026 तक भंडार $701.4 बिलियन तक पहुंच गया, जो 11 महीने के आयात के लिए पर्याप्त है।
कृषि और ग्रामीण परिवर्तन:
- रिकॉर्ड उत्पादन: वर्ष 2024-25 के लिए खाद्यान्न उत्पादन 3577.3 LMT रहने का अनुमान है।
- DBT का लाभ: पीएम-किसान (PM-Kisan) योजना के तहत अब तक किसानों को ₹4.09 लाख करोड़ से अधिक जारी किए जा चुके हैं।
- मनरेगा सुधार: विकसित भारत-ग्रामजी (Viksit Bharat-GramG) पहल का प्रस्ताव ग्रामीण रोजगार को 2047 के विजन से जोड़ने के लिए रखा गया है।
उद्योग, बुनियादी ढांचा और नवाचार:
- PLI का प्रभाव: उत्पादन आधारित प्रोत्साहन (PLI) योजनाओं ने ₹2.0 लाख करोड़ का निवेश आकर्षित किया और 12.6 लाख रोजगार पैदा किए।
- सेमीकंडक्टर: भारत सेमीकंडक्टर मिशन के तहत ₹1.60 लाख करोड़ के निवेश वाली 10 परियोजनाएं आगे बढ़ रही हैं।
- परिवहन: उच्च गति वाले गलियारे (High-speed corridors) 2014 के 550 किमी से बढ़कर 2026 में 5,364 किमी हो गए हैं।
ऊर्जा, अंतरिक्ष और प्रौद्योगिकी:
- नवीकरणीय ऊर्जा (Renewables): भारत अब कुल नवीकरणीय ऊर्जा और सौर क्षमता में वैश्विक स्तर पर तीसरे (3rd) स्थान पर है।
- स्पेस फ्रंटियर: भारत स्वायत्त उपग्रह डॉकिंग (SPADEX) क्षमता हासिल करने वाला दुनिया का चौथा देश बन गया है।
सामाजिक क्षेत्र, शिक्षा और स्वास्थ्य:
- शिक्षा: भारत में अब 23 IIT, 21 IIM और 20 AIIMS हैं। साथ ही जंजीबार और अबू धाबी में अंतरराष्ट्रीय IIT परिसर भी खुल चुके हैं।
- गरीबी उन्मूलन: बहुआयामी गरीबी सूचकांक (MPI) 2005-06 के 55.3% से गिरकर 2022-23 में 11.28% पर आ गया है।
रणनीतिक दृष्टिकोण: “अनुशासित स्वदेशी” (Disciplined Swadeshi):
सर्वेक्षण में रणनीतिक लचीलेपन के लिए तीन-स्तरीय रणनीति का प्रस्ताव दिया गया है:
- महत्वपूर्ण क्षमताओं का निर्माण: स्वदेशी उच्च तकनीक क्षेत्रों का विकास।
- इनपुट लागत को कम करना: विनिर्माण दक्षता बढ़ाना।
- रणनीतिक अपरिहार्यता: वैश्विक आपूर्ति श्रृंखलाओं में भारत को एक अनिवार्य कड़ी बनाना।
October 17, 2025
October 16, 2025
October 6, 2025
September 24, 2025
