December 13, 2025
Dedicated Freight Corridors (DFCs):
The Indian Railways’ High Density Network carries the bulk of the national transport’s load. The railways should focus more on decongesting and increasing the capacity of this section, according to Mangal Dev, Head of Hitachi Rail (Mobility) and Director of Hitachi India Pvt. Ltd.
Why is it important to decongest the railways’ high density networks?
During the preparation of the National Rail Plan, the networks were categorised into high density network (HDN) and highly utilised network (HUN). This means that if a section can run 100 trains a day, you are running more than 100 trains. Because of this, the whole system gets tired and there is no time for maintenance, which affects efficiency and compromises safety.
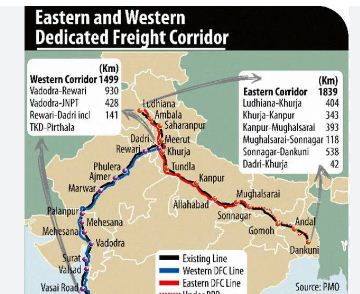
Dedicated Freight Corridors (DFCs): Eastern & Western –
High Density Network (HDN) and Highly Utilised Network (HUN):
Indian Railways’ High Density Network (HDN) and Highly Utilised Network (HUN) carry a major share of the national transport load. Reducing congestion and enhancing capacity on these corridors is essential.
What are HDN and HUN?
Under the National Rail Plan, the railway network was classified into HDN and HUN:
HDN (High Density Network):
- Highly busy routes connecting major metro cities.
- Approx. 11,000 km, covering 7 major corridors.
HUN (Highly Utilised Network):
- Routes with high utilisation and multiple origin–destination flows.
Traffic Load
- Together, HDN + HUN constitute ~16% of the total network,
- But they carry 41% of total railway traffic.
Capacity Stress Example:
If a section has a capacity of 100 trains/day, but more than 100 trains are running:
- No time left for maintenance
- Efficiency drops
- Safety risks increase
To address this, the government is approving multiple multi‑tracking projects to reduce congestion.
Importance of Eastern and Western DFCs:
These corridors are designed to decongest HDN/HUN. By shifting freight trains to separate tracks, passenger trains can run faster, safer, and more punctually.
Eastern Dedicated Freight Corridor (EDFC):
- Length: ~1,337–1,856 km (Ludhiana, Punjab → Dankuni, West Bengal)
- Status (Dec 2025): Fully operational (100%)
- Major freight: Coal, steel, foodgrains, fertilizers
- Key benefit: Coal transport time from eastern coalfields to northern thermal power plants has reduced by nearly half.
Western Dedicated Freight Corridor (WDFC):
- Length: ~1,506 km (Dadri, Uttar Pradesh → JNPT, Navi Mumbai)
- Status (Dec 2025): Final section (Vaitarna–JNPT, ~102 km) to be commissioned by Dec 2025 → Overall 93–96% operational
- Major freight: Containers, imported coal, fertilizers
- Key benefits:
- Faster connectivity from ports to northern hinterland
- Double‑stack container trains enabled
Recent Progress (as of 2025):
- Total DFC network: Out of ~2,843 km, ~2,741 km is operational
- Daily trains: ~400–480 trains; at full capacity, one train every 10 minutes is possible
- Benefits:
- Lower logistics cost
- Rail freight share moving toward the 45% target
- Future corridors proposed:
- East Coast DFC
- East–West DFC
- North–South DFC
पूर्वी और पश्चिमी समर्पित मालवाहक गलियारे (Dedicated Freight Corridors – DFCs)
भारतीय रेलवे की उच्च घनत्व नेटवर्क (High Density Network – HDN) और उच्च उपयोग नेटवर्क (Highly Utilised Network – HUN) राष्ट्रीय परिवहन भार का बड़ा हिस्सा वहन करती हैं। इन गलियारों में भीड़भाड़ कम करने और क्षमता बढ़ाने पर अधिक ध्यान केंद्रित करना चाहिए।
HDN और HUN क्या हैं?
राष्ट्रीय रेल योजना (National Rail Plan) के दौरान नेटवर्क को उच्च घनत्व नेटवर्क (HDN) और उच्च उपयोग नेटवर्क (HUN) में वर्गीकृत किया गया।
- HDN: मुख्य रूप से मेट्रो शहरों को जोड़ने वाले व्यस्त मार्ग (लगभग 11,000 किमी, 7 प्रमुख गलियारे)।
- HUN: बहु-उत्पत्ति/गंतव्य वाले उच्च उपयोग वाले मार्ग। ये मिलकर कुल नेटवर्क का ~16% हैं लेकिन 41% यातायात वहन करते हैं। यदि किसी खंड की क्षमता 100 ट्रेनें/दिन है, तो उस पर 100 से अधिक ट्रेनें चल रही हैं → इससे रखरखाव का समय नहीं मिलता, दक्षता प्रभावित होती है और सुरक्षा समझौता होती है। सरकार अब कई मल्टी-ट्रैकिंग परियोजनाओं को मंजूरी दे रही है ताकि इन खंडों की भीड़भाड़ कम हो।
पूर्वी और पश्चिमी DFCs का महत्व
ये गलियारे HDN/HUN की भीड़भाड़ कम करने के लिए बनाए गए हैं। मालगाड़ियों को अलग ट्रैक मिलने से यात्री ट्रेनें तेज और समयबद्ध चल सकेंगी।
✅ पूर्वी समर्पित मालवाहक गलियारा (Eastern DFC – EDFC)
- लंबाई: ~1,337-1,856 किमी (लुधियाना, पंजाब से दानकुनी, पश्चिम बंगाल तक)।
- स्थिति (दिसंबर 2025): पूरी तरह चालू (100% ऑपरेशनल)।
- मुख्य यातायात: कोयला, इस्पात, खाद्यान्न, उर्वरक।
- लाभ: पूर्वी कोयला खदानों से उत्तरी थर्मल पावर प्लांटों तक कोयला परिवहन समय आधा हो गया।
✅ पश्चिमी समर्पित मालवाहक गलियारा (Western DFC – WDFC)
- लंबाई: ~1,506 किमी (दादरी, उत्तर प्रदेश से JNPT, नवी मुंबई तक)।
- स्थिति (दिसंबर 2025): अंतिम खंड (वैतरना-JNPT, ~102 किमी) दिसंबर 2025 में चालू होने वाला है; कुल ~93-96% चालू।
- मुख्य यातायात: कंटेनर, आयातित कोयला, उर्वरक।
- लाभ: बंदरगाहों से उत्तरी हिंद महासागर तक तेज कनेक्टिविटी; डबल-स्टैक कंटेनर ट्रेनें।
हाल की प्रगति (2025 तक)
- कुल DFC नेटवर्क: ~2,843 किमी में से ~2,741 किमी चालू।
- दैनिक ट्रेनें: ~400-480 (क्षमता तक पहुंचने पर हर 10 मिनट में एक ट्रेन संभव)।
- लाभ: लॉजिस्टिक्स लागत कम, रेल का माल ढुलाई हिस्सा बढ़कर ~45% लक्ष्य की ओर।
- आगे: ईस्ट कोस्ट, ईस्ट-वेस्ट और नॉर्थ-साउथ जैसे नए गलियारे प्रस्तावित।
निष्कर्ष
EDFC और WDFC की पूर्णता से HDN/HUN की भीड़भाड़ कम होगी, माल ढुलाई तेज और सस्ती होगी, तथा यात्री सेवाएं बेहतर होंगी। मल्टी-ट्रैकिंग और नए गलियारे इस दिशा में महत्वपूर्ण कदम हैं।
October 17, 2025
October 16, 2025
October 6, 2025
September 24, 2025
