July 7, 2025
BRICS 2025 Rio Summit: Major Declarations
Why in News? The 11-member BRICS group, at Rio Summit 2025 ,comprising key emerging economies, issued a strong condemnation of the terrorist attack in Pahalgam, Jammu and Kashmir.
Relevance : UPSC Pre & Mains
Prelims : BRICS/NDB/CRA
Mains : GS 2
The Rio Declaration emphasized:
- Zero Tolerance for Terrorism: BRICS nations reaffirmed their commitment to combating terrorism in all its forms, including cross-border movement, financing, and safe havens.
- Call for UN Action: The declaration urged the expeditious finalization and adoption of the Comprehensive Convention on International Terrorism within the UN framework.
- Rejection of Double Standards: The group stressed a unified approach to counter-terrorism, rejecting any double standards, aligning with India’s stance against Pakistan’s support for cross-border terrorism and China’s shielding of UN-banned terrorists.
Support for UN Security Council Reform:
The Rio Summit adopted its strongest-ever language on UN Security Council (UNSC) reform, advocating for a more democratic, representative, effective, and efficient UNSC.
Key points include:
- Increased Representation: The declaration called for enhanced representation of developing countries to amplify the voice of the Global South.
- Support for Brazil and India: China and Russia, as permanent UNSC members, reiterated their support for Brazil and India to play a greater role in the UN, explicitly including the UNSC, building on the 2022 Beijing and 2023 Johannesburg Declarations.
- Global South Advocacy: A reformed UNSC was highlighted as essential to strengthening the influence of developing nations.
- Balancing Act for India: India’s endorsement reflects its delicate balancing act, having previously joined BRICS in condemning Israel’s actions at the June 2024 foreign ministers’ meeting and the Kazan Summit.
Opposition to Unilateral Economic Sanctions:
BRICS voiced serious concerns about unilateral tariff and non-tariff measures that distort trade and violate WTO rules, implicitly addressing the Trump administration’s policies:
- International Law Violation: The declaration stated that unilateral coercive measures, such as economic sanctions, are contrary to international law and have far-reaching negative implications.
- Global Trade Concerns: While some members hesitated to name the US, the group collectively criticized measures that undermine fair trade practices.
Focus on Climate Finance and IMF Reforms:
The Rio Summit also emphasized:
- Concessional Climate Finance: BRICS called for increased climate finance from Western nations to support sustainable development.
- IMF Reforms: The group backed reforms to strengthen the International Monetary Fund’s role in global economic governance.
- New Development Bank (NDB): The declaration highlighted the NDB’s growing role in supporting infrastructure and development projects in emerging economies.
India’s Key Takeaways:
- Counter-Terrorism: The strong anti-terrorism stance aligns with India’s push for global cooperation against terrorism, particularly targeting Pakistan’s cross-border activities.
- UNSC Aspirations: The explicit support for India’s greater role in the UNSC marks a significant diplomatic win, reinforcing its global leadership ambitions.
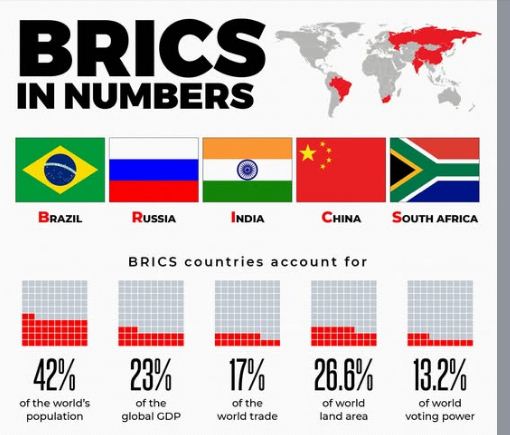
About BRICS :
BRICS is an intergovernmental organization comprising Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa. Formed as BRIC in 2006, it expanded to include South Africa in 2010, becoming BRICS. The group promotes cooperation among major emerging economies and aims for a multipolar world order.
First Established Members:
- Brazil
- Russia
- India
- China
- South Africa (joined 2010)
Contributions:
Global GDP
- Nominal GDP: ~$28 trillion, ~27% of global GDP (2024).
Population:
- over 40% of global population (2023).
Trade:
- ~16% of global trade (2021); BRICS+ (with new members) at 22% of merchandise exports (2023).
Key Initiatives:
New Development Bank (NDB):
- Established 2014, operational 2015.
- Finances infrastructure and sustainable development.
- Capital: $50 billion (initial), expanded to $100 billion.
- Approved $32 billion for 96 projects (e.g., clean energy, transport).
Contingent Reserve Arrangement (CRA):
- Established 2014, active 2015.
- $100 billion fund for currency crisis support.
- China contributes 41%.
Common Currency and Payment Systems:
- Promotes local currency trade to reduce U.S. dollar reliance.
- Developing alternatives to SWIFT (e.g., China’s CIPS, Russia’s SPFS, India’s SFMS, Brazil’s Pix).
- 2023 Summit: Working group for a potential BRICS currency.
Economic and Trade Cooperation:
- BRICS Economic Partnership Strategy boosts intra-BRICS trade.
- Digital Economy Working Group supports digital trade (15.5% of global GDP).
- Focus on energy, agriculture, and green initiatives.
Cultural and People-to-People Cooperation:
- BRICS Network University, Academic Forum, and Think Tank Council.
- BRICS Film Festival, Games, and cultural exchanges.
- Remote Sensing Satellite Constellation and Energy Research Platform.
Political and Security Cooperation:
- Advocates UN, WTO, and Bretton Woods reforms.
- Addresses counterterrorism, cybersecurity, and anti-corruption.
- Coordinates in G20.
BRICS Expansion:
- 2023: Added Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran, Saudi Arabia, UAE (Argentina declined).
- 2024: Partner country category (e.g., Algeria, Indonesia, Turkey).
- BRICS+ now ~46% of global population, 35.6% of GDP (PPP).
Challenges:
- Diverse political systems and priorities.
- China’s dominance (~70% of GDP).
- Geopolitical tensions (e.g., India-China).
- Limited trade integration compared to EU.
- Perceived as anti-Western by some.
Conclusion:
BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa) contributes ~27% of global nominal GDP, 35% of GDP (PPP), and over 40% of the world’s population. Initiatives like the NDB, CRA, and local currency trade aim to enhance economic and political influence. Expansion to BRICS+ strengthens its global role, but internal diversity and tensions pose challenges.
January 30, 2025
January 20, 2025
January 14, 2025
