September 23, 2025
CPCB Report: 7 Dramatic Gains in India’s River Pollution Fight
 CPCB Report (2023)
CPCB Report (2023)
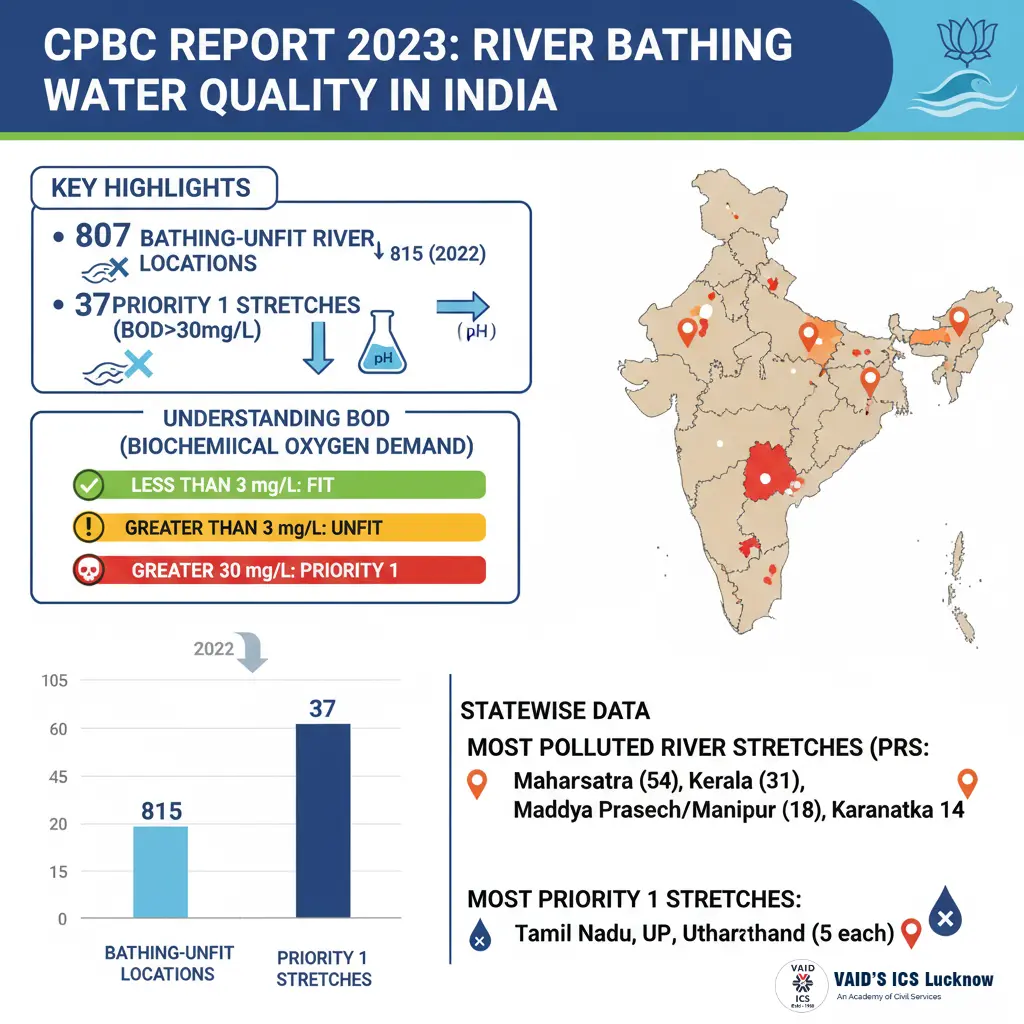
As per a report by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), the count of bathing-unfit sites in Indian rivers declined slightly from 815 in 2022 to 807 in 2023.
Key Highlights of the CPCB Report (2023)
Released by: Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB)
Objective: Monitor river health through Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) levels.
Overall Improvement:
Unfit to bathe locations
- 2023: 807 locations
- 2022: 815 locations
- Improvement: 8 fewer polluted locations.
Most polluted river stretches (‘Priority 1’)
- 2023: 37 stretches
- 2022: 45 stretches
- Indicates some progress in cleaning critical stretches.
Understanding BOD:
BOD (Biological Oxygen Demand):
- Indicator of organic matter in water.
- Low BOD = healthy river
- BOD > 3 mg/L: Water unfit for bathing.
- BOD > 30 mg/L: Classified as Priority 1 — most polluted, needing urgent action.
River Health Data:
Polluted River Stretches (PRS):
- 2023: 296 stretches in 271 rivers.
- 2022: 311 stretches in 279 rivers.
- State-wise data (2023):
Highest polluted stretches:
- Maharashtra – 54
- Kerala – 31
- Madhya Pradesh – 18
- Manipur – 18
- Karnataka – 14
Highest ‘Priority 1’ stretches (BOD > 30 mg/L):
- Tamil Nadu – 5
- Uttar Pradesh – 5
- Uttarakhand – 5
2022 comparison:
- Gujarat & Uttar Pradesh had 6 Priority 1 stretches each.
- Maharashtra topped with 55 polluted stretches, followed by:
- Madhya Pradesh – 19
- Bihar – 18
- Kerala – 18
- Karnataka – 17
- Uttar Pradesh – 17
About Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) :
- Established: 1974
- Established Under: Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974
- Statutory Status: Yes, it is a statutory organization.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC)
- Parent Body: The National Green Tribunal (NGT) acts as a judicial authority, while CPCB functions as a regulatory body.
Key Functions of CPCB:
CPCB performs both advisory and regulatory roles at the national level.
Under the Water Act, 1974:
- Advise the Central Government on matters related to water pollution.
- Coordinate activities of State Pollution Control Boards (SPCBs).
- Plan and implement nationwide water pollution control programs.
- Set water quality standards for rivers, lakes, and other water bodies.
- Provide technical assistance and training to SPCBs.
Under the Air Act, 1981:
- Set air quality standards for the entire country.
- Monitor and regulate emissions from industries and vehicles.
- Advise on the control and prevention of air pollution.
- Conduct research and development (R&D) on pollution control technology.
Under the Environment Protection Act, 1986:
- Waste Management Oversight:
- Hazardous waste, biomedical waste, municipal solid waste, e-waste, plastic waste, etc.
- Issue directions to industries for environmental compliance.
- Act as a central agency for the implementation of national environmental laws.
September 23, 2025
September 22, 2025
September 17, 2025
September 16, 2025
