September 8, 2025
Inverted Duty Structure (IDS): 5 Major GST Industry Issues
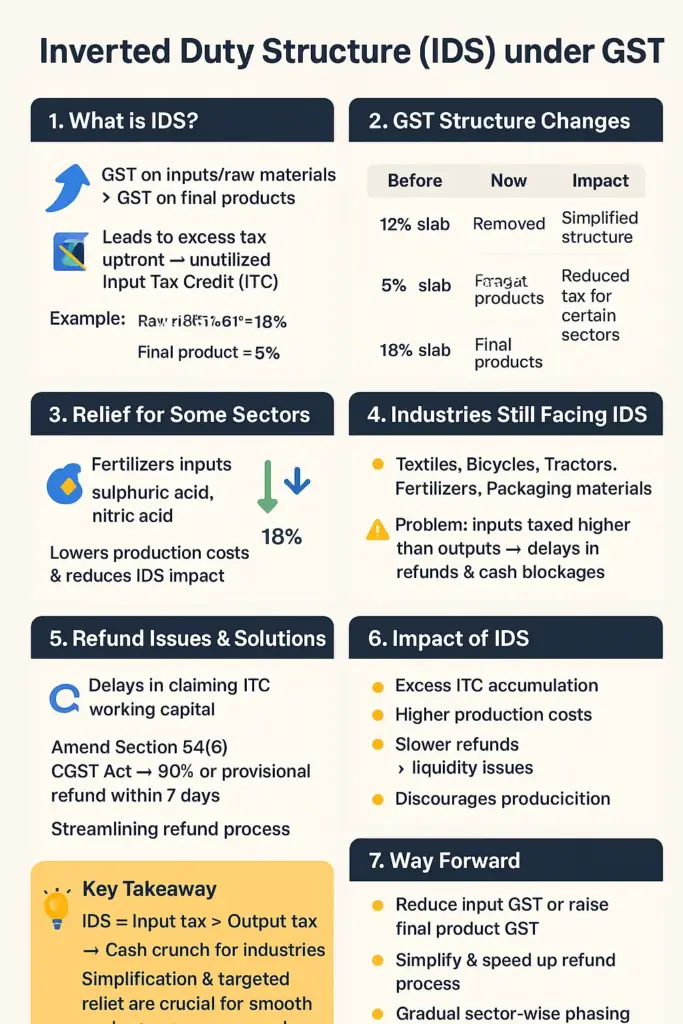
The inverted duty structure (IDS)
The inverted duty structure (IDS) under GST has been a long-standing issue for several industries like textiles, bicycles, tractors, and fertilizers.
- Recently, the GST Council reduced rates on certain inputs to address the inversion problem, bringing some relief.
- However, gaps still remain, particularly for sectors where input tax rates are higher than output tax rates, leading to working capital blockages and refund-related issues.
- The Council is also working on legal amendments to streamline the refund process and reduce cash flow problems for industries.
Key Points: The inverted duty structure (IDS)
GST Structure Change:
GST now has a two-slab structure:
- 5% slab – for essential goods and raw materials.
- 18% slab – for final products.
Earlier, there was a 12% slab, which has now been removed.
Relief for Some Sectors:
- Reduction in GST rates for certain fertilizer inputs like sulphuric acid, nitric acid, and ammonia from 18% to 5%.
- This is expected to lower production costs for fertilizers.
Industries Still Facing Inversion:
Textiles, bicycles, tractors, fertilizers, and certain packaging materials are still facing IDS problems.
Example:
- Raw materials taxed at 18%.
- Final product taxed at 5%.
- This leads to discrepancies in tax rates and difficulties in processing refunds.
Refund Issues:
- Industries face delays and cash blockages due to complex refund procedures.
GST Council has proposed:
- Amending Section 54(6) of the CGST Act to allow 90% of the provisional refund to be issued within seven days.
- Streamlining refund mechanisms to prevent working capital shortages.
Concerns for Industries:
- High tax rates on inputs discourage production.
- Difficulty in claiming refunds adds to financial stress.
- Industries seek a streamlined and effective refund process to prevent funds from being tied up.
About Input-Output GST (Inverted Duty Structure):
An Inverted Duty Structure (IDS) occurs when the GST levied on inputs is higher than that applied to the final product.
- This causes businesses to pay more tax upfront, leading to unutilized Input Tax Credit (ITC).
Example:
- GST on raw material (input) = 18%
- GST on finished product (output) = 5%
- The company pays 18% initially, but only collects 5% from customers, creating an imbalance.
Impact:
- Excess ITC accumulation.
- Increased working capital requirement.
- Higher production costs.
- Slower refunds affecting business liquidity.
Way Forward:
- Reduce input GST rates or increase final product GST rates to balance tax rates.
- Simplify and speed up refund processes.
- Gradual phasing out of IDS by revising GST rates sector-wise.
- Digital solutions for real-time refund tracking to support industries.
September 9, 2025
September 8, 2025
September 4, 2025
September 1, 2025