December 18, 2025
What is Weakly Interacting Massive Particles ( WIMPS) ?
Why in News ?Astronomers are debating whether a recent study offers the first direct evidence of dark matter — the invisible substance making up ~27% of the universe — or is yet another false alarm.
- In a paper published November 2025 in the Journal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics, University of Tokyo researcher Tomonori Totani analyzed 15+ years of NASA Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope data.
- He identified a halo-like excess of ~20 GeV gamma rays around the Milky Way’s center, matching predictions for annihilation of weakly interacting massive particles (WIMPs) — a leading dark matter candidate.
- If confirmed, this would reveal dark matter as a new particle beyond the Standard Model, solving a mystery dating to Fritz Zwicky’s 1930s observations of galaxy clusters needing “missing mass” for gravitational stability.
WIMPs, or Weakly Interacting Massive Particles, are a leading theoretical class of subatomic particles proposed to explain the mystery of dark matter. Although they haven’t been directly observed yet, they are the focus of some of the most sensitive experiments in modern physics.
What are WIMPs?
WIMPs are hypothetical particles that do not belong to the “Standard Model” of physics (the current list of known particles like electrons and quarks). They are defined by three primary characteristics:
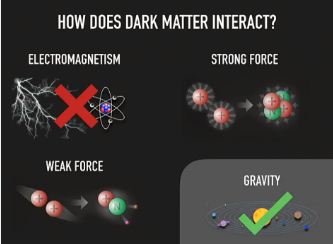
- Weak Interactions: They do not interact with the electromagnetic force. This means they do not emit, absorb, or reflect light, making them invisible to telescopes. They only interact via gravity and the weak nuclear force.
- Massive: Despite the name “wimp,” they are actually quite heavy. Scientists estimate they could be 1 to 1,000 times more massive than a proton.
- Slow-Moving (“Cold”): Because of their large mass, they move relatively slowly compared to the speed of light. This allows them to clump together under gravity, forming the “scaffolding” that holds galaxies together.
The “WIMP Miracle”: Physicists discovered that if a particle with these specific properties existed in the early universe, the amount of them left over today would almost exactly match the amount of dark matter we observe. This striking coincidence is why WIMPs became the top candidate for dark matter.
What is Dark Matter?
Dark matter is a substance that does not emit, absorb, or reflect light (electromagnetic radiation). This makes it completely invisible to traditional telescopes. However, it has mass and exerts a massive gravitational pull.
- The 5% Rule: Everything you have ever seen—stars, planets, trees, people, and atoms—makes up less than 5% of the universe.
- The Dark Majority: Dark matter makes up about 27% of the universe. The remaining 68% is “dark energy,” a different mystery that is causing the universe to expand faster.
October 17, 2025
October 16, 2025
October 6, 2025
September 24, 2025
