November 1, 2025
Types of Orbits: What is Low Earth Orbit (LEO)? LEO/MEO/GEO
Satellites circle the Earth on various paths based on their applications, altitudes, and coverage. The primary types of orbits are:
1. Low Earth Orbit (LEO):
Altitude: 160–2000 km above the Earth
Characteristics: Short orbital period (~90–120 minutes), moving fast
Applications: Earth observation, remote sensing, weather satellites, and some communication satellites (Starlink).
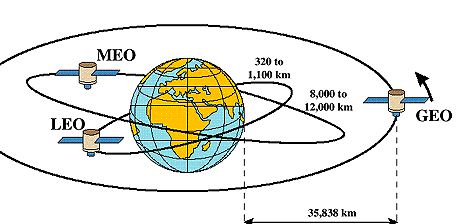
2. Medium Earth Orbit (MEO):
Altitude: 2000–35,786 km
Characteristics: Longer orbital period than LEO, stable for navigation satellites.
Applications: GPS, GLONASS, Galileo navigation satellites.
3. Geosynchronous orbit (GSO):
Altitude: ~35,786 km
Characteristics: Returns to the same position in the same time every day.
Applications: Weather forecasting, communication satellites.
4. Geostationary Orbit (GEO):
Altitude: ~35,786 km, directly above the equator.
Characteristics: Appears to be stationary in relation to the Earth; orbital period = 24 hours.
Applications: Television, internet, and long-distance communication satellites.
NOTE: While all GEO satellites are geosynchronous, not all geosynchronous satellites are GEO as they can be in inclined orbits that would cause the satellite to “figure-eight” in the sky.
5. Sun-Synchronous Orbit (SSO):
Altitude: ~600–800 km (typically LEO).
Characteristics: Passes over the same part of Earth at the same local solar time.
Applications: Remote sensing, Earth observation, and spy satellites.
6. Polar Orbit:
Path: Passes over the poles of the Earth.
Characteristics: Can cover the entire surface of the Earth over multiple orbits.
Applications: Earth mapping, reconnaissance, and monitoring of the climate/weather.
7. Transfer Orbits:
Example: Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO).
Purpose: Transfer orbit models how to place a satellite into a final operational orbit.
October 17, 2025
October 16, 2025
October 6, 2025
September 24, 2025
